Intro to GKE
Kubernetes is an open-source platform for managing containerized workloads and services. K8s or K8 (as it is colloquially known) makes it easy to orchestrate different containers on different hosts, scale them as microservices, deploy rollouts or rollbacks etc. K8s was open-sourced by Google in 2014. Below are some of the advantages of using K8s
- Load balancing & service discovery: K8s can expose your a container to outside traffic. If incoming traffic is high, it can load balance and distribute so the deployment is stable.
- Storage orchestration - allows you to declaratively mount a storage system (local or cloud store)
- Structured rollout and rollbacks - you can instruct K8s your desired system state and it can control the update of the container images in a controlled manner.
- Automatic resource allocation - you provide K8s a set of nodes (a cluster) and you specify how much CPU and memory each container needs. K8s takes care of efficiently running all of the containers in the provided node pool.
- Self-healing - K8s can automatically divert traffic from unresponsive containers, kill them, restart them and advertise only after they recover
- Secret management - you can store & manage sensitive info like passwords, SSH keys, oAuth tokens separately from container images
Components of a Kubernetes cluster
- Node - a physical machine that runs containers (with on-prem set up). In a cloud set up, this could be a VM.
- Cluster - a set of such nodes together running an application. A cluster can have a group of nodes that run as control plane and the remaining running as nodes for containers.
- Node pool - designate subset of nodes within a cluster.
- Pod - a process running a container (with a wrapper around it). Pods are the smallest unit of reference in K8. Usually only one container runs in a pod. But you can package more than 1 container, especially if they have to communicate or share resources. A pod can provide a unique IP per pod and different ports for different containers running within it. To interact with a pod, you can use the
kubectlcommand.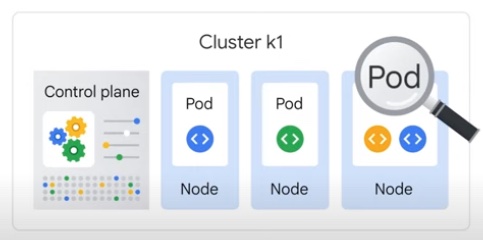
- To see the list of pods in your cluster, run
kubectl get pods
The IP address of a pod can change over time, especially as pods are created and terminated over time. Thus if the front-end pods refer to back-end pods by IP, the application may break. This is why you wrap the relevant pods behind a service and give it a fixed IP. As you scale your app, any number of pods can share that IP of that service.
You can use kubectl commands to create pods, create load balancer, network etc. However, k8 allows you to declaratively define your architecture in a Yaml file, called a deployment config file.
The control plane
The control plane makes decisions about the cluster by detecting and responding to cluster events. The control plane can ideally be run on any node in the cluster. However, by convention, cluster start-up scripts start control plane first and do not run any user containers on that node.
- kube-apiserver is the API server component of the control plane which exposes K8 via the K8 API.
- etcd - is a consistent, highly available key-value store that stores all data about the cluster
- kube-scheduler - watches newly created pods with no assigned node and selects a node for them to run on. The scheduler will take into account the resource requirements, affinity specifications, data locality etc.
- kube-controller-manager - fine grained controller component that listens to events happening in the cluster.
- cloud-controller-manager - allows you to link your k8 cluster into the cloud provider's API.
Components of a Node
These components run on every node (physical or virtual worker machine) providing a kubernetes runtime environment.
- kubelet - agent that runs on every node. It makes sure that containers are running in a pod.
- kube-proxy - maintains network rules on each node. This network allows communication within the cluster or from outside to your cluster.
- Container runtime - responsible for running the container.
Google Kubernetes Engine
GKE is a managed K8 in the cloud. It is a bunch of compute engine instances that are bound together to form a cluster. This cluster can be created using web UI or gcloud CLI. When using GKE, Google provides a built-in load-balancer service.